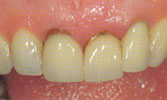
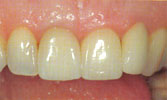
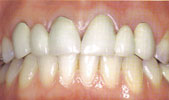
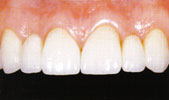
Dentures
A denture replaces missing teeth and adjacent tissues. Unlike dental implants, a denture is removable.
Benefits of Dentures
- Prevents exisiting teeth from drifting into surrounding space of the missing teeth
- Teeth out of position can damage tissues in the mouth
- Helps to chew food
Types of Dentures
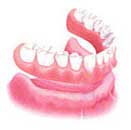
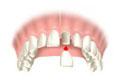
Complete dentures or Full dentures are used when all the teeth are missing . Complete dentures can be either "conventional" or "immediate". The framework of complete dentures may be made of resin, metal or a combination.
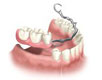
Implant supported overdentures are an alternate to conventional dentures whereby a full dentures is placed over the dental implants with metal bar/balls that gives better retention.
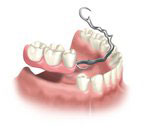
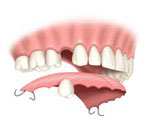
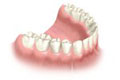
Partial dentures are used when some natural teeth remain.
A removable partial denture usually consists of replacement teeth attached to a pink or gum-colored plastic base, which is connected by metal clasps or precision attachments that holds the denture in place in the mouth. Precision attachments are generally more esthetic than metal clasps and they are nearly invisible.
Conventional Dentures and Immediate Dentures
Conventional Dentures are made after the teeth have been removed and the gum tissue has begun to heal. Conventional dentures is ready for placement in the mouth about 8 to 12 weeks after the teeth have been removed.
Immediate dentures are made in advance and can be positioned as soon as the teeth are removed. As a result, the wearer does not have to be without teeth during the healing period. However, bones and gums shrink over time, especially during the healing period following tooth removal therefore immediate dentures would usually require more adjustments to fit properly during the healing process and generally should only be considered a temporary solution until conventional dentures can be made. The healing process as it can take months for your bone and tissue to stabilize after tooth extractions.
Procedure for Conventional Dentures Treatment
1.First Evaulation and dentures site preparation
- if tooth extraction is required, the teeth are extracted and left to heal
- 2.Making the dentures
- Once the gums are healed and healthy, an impression of the mouth is taken for a wax-up
- The wax-up is used to determine the most optimal position of the jaw and teeth dimensions (size, shape, length, width)
- The wax up is sent to a dental laboratory to construct a "try-in" set of denture
3.Trial of "try-in" set of dentures and re-adjustments
- The "try-in' denture are placed in the mouth to assure comfort, fit, bite position and appearance
- The "try-in" dentures are re-worked in the labs and trail fitted during next visits until the color, shape and proper fit is obtained for the final set of dentures to be cast
4.Fitting of final dentures
For immediate dentures, impression-taking and the wax-up is first done before tooth extraction.
Recovery Expectations
Recovery from getting dentures may be a two-step process. If extractions are necessary, patients can expect the recovery of their gums to take up to 4 weeks or longer.
Once healed and the dentures are placed, the patient will need time to adjust to the new teeth. While patients can speak normally within a few hours, they may experience minor discomfort when eating or chewing. This discomfort may last from several days to a few weeks until the muscles of your cheek and tongue learn to keep them in place and you get comfortable inserting and removing them. It is recommended that patients with new dentures eat soft foods until they become comfortable with chewing.
it is not unusual for minor irritation or soreness to occur and for saliva flow to increase when you first start wearing dentures, but these problems will diminish as your mouth adjusts to the new denture.
Care for Dentures
- Dentures should be removed at night to give the gums a rest and to reduce the pressure on the underlying bone or as directed by your dentist
- Regular denture care includes brushing your denture with a denture brush and a denture paste after eating. Dentures can collect plaque and food stains
- Keep your dentures in water to avoid drying out and distorting.
- Dentures can and may break if dropped onto a hard surface, thus becareful when handling them.
- Clean and massage your gums and tongue with a regular soft-bristled toothbrush to help keep them healthy